

Problem 1
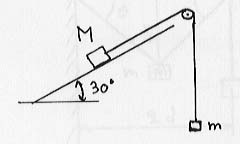
A block of mass M=4 kg resting on a 30° incline is attached
to a second block of mass m by a massless cord that passes over
a frictionless peg as shown. The static coefficient of friction between
the block and the incline is ![]() s
= 0.4.
s
= 0.4.
Problem 2
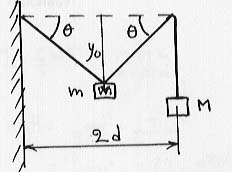
A first block of mass M is attached to the end of a very long
rope hung over a peg at a distance 2d from the wall; the other end
is attached to the wall at the same height as the peg. A second block of
mass m is attached to the middle of the string, half way between
the wall and the peg (see picture). It follows that the included angles
between the rope and the horizontal at the wall and at the peg have a magnitude
![]() . Isolating the forces acting on
m and M, find at what vertical distance yo
the system is in equilibrium.
. Isolating the forces acting on
m and M, find at what vertical distance yo
the system is in equilibrium.
Problem 3
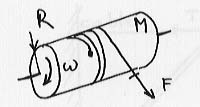
A homogeneous cylinder of mass M=100 kg and radius R=0.3 m is mounted such that it turns without friction and clockwise around its fixed symmetry axis. It is rotated by a drive belt that wraps around its perimeter and exerts a constant torque (see figure). At time t=0, its angular velocity is zero. At time t=30 s, its angular velocity is 10 rev/s. For a cylinder I= ½ MR².
Problem 4
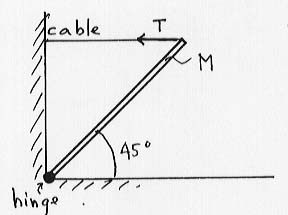
A uniform boom of length L=5 m and total mass M=150 kg is connected to the ground by a hinge at the bottom, makes an angle 45° with the horizontal and is supported by a horizontal cable attached at the top as shown.
Problem 5
The mass of Saturn is M = 5.69x1026 kg
The universal gravitation constant is G = 6.67x10-11N·m²/kg².
Problem 6
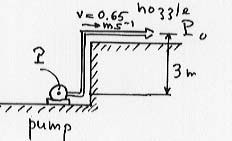
Water flows in a laminar way and without friction through a 3 cm diameter hose at speed v=0.65 m/s. The hose terminates at one end into a nozzle of diameter 0.3 cm, and the other end it is connected to a water pump.
Problem 7
A mass M=2 kg oscillates horizontally with an initial amplitude A0=3 cm on a spring of force constant k=400 N/m. The damping is weak!
Problem 8
A typical loud sound wave with a frequency of 1 kHz has a pressure amplitude
of 10-4 atm (1 atm ~105 Pa and ![]() air
= 1.29 kg m-3). Use the value v=343 m/s for the speed
of sound propagation in air at 200° C.
air
= 1.29 kg m-3). Use the value v=343 m/s for the speed
of sound propagation in air at 200° C.