
Physics 101 - Final Exam 1998
Lecturer: D.S. Armstrong
Problem 1
-
A coin of mass = 4 g lies on a copy of your physics textbook,
which is being tilted at an angle
 with respect to the
horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the coin and the
book is µs = 0.4 and the coefficient of kinetic friction
is µk = 0.3.
with respect to the
horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the coin and the
book is µs = 0.4 and the coefficient of kinetic friction
is µk = 0.3.
-
a) Find the maximum angle
 at which the book can be tilted before
the coin will start to slide.
at which the book can be tilted before
the coin will start to slide.
-
b) Assume the book is tilted at an angle of 73°. What
will be the kinetic energy of the coin after it has a slid a distance
l = 15 cm along the cover of the book?
-
c) How long did it take for the coin to slide the distance l?
Problem 2
-
A child on rollerblades catches a ball that has a mass of m1 =
0.25 kg. The initial velocity of the ball is v1 = (10 m/s)i
and the initial velocity of the child is zero. The mass of the child
(including her rollerblades) is m2 = 30 kg. Ignore gravity and air
resistance.
- a) What is the velocity of the child immediately after she catches
the ball?
- b) What is the change in the total mechanical energy when the
child catches the ball?
Problem 3
-
An object is projected from the surface of the Earth with an initial speed
equal to three times the escape velocity. What is the speed of the object
when it is very far from the Earth? Neglect air resistance.
The radius of the Earth is 6370 km, its mass is 5.98 x 1024 kg,
G = 6.67 x 10-11 N m2/ kg2.
Problem 4
-
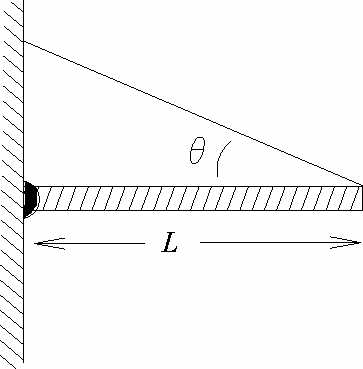 A flagpole of mass m and length L is hinged at
a wall and supported in a horizontal position by a
massless cable attached to the free end (see diagram).
The cable makes an angle
A flagpole of mass m and length L is hinged at
a wall and supported in a horizontal position by a
massless cable attached to the free end (see diagram).
The cable makes an angle  with the horizontal.
with the horizontal.
- a) What is the tension in the cable?
- b) What is the (vector) force exerted on the flagpole by the hinge?
- c) What is the direction of the torque (about the hinge point)
that the tension in the cable exerts on the flagpole?
Problem 5
-
A transverse wave has the form
-
y = 10 sin(0.01x - 20t)
-
where x, y have units of meters, and t has units of seconds.
- a) What is the wavelength and frequency of this wave?
- b) What is the magnitude and direction of the wave velocity?
- c) What is the value of y for x = 20 m at time t = 0.05 s?
- d) What are the maximum values of dy/dt and
dy/dx ?
Problem 6
-
A police car, travelling at 120 km/hr, passes a pedestrian. The siren is
on, emitting a sound of frequency 360 Hz. What is the frequency of the
sounds the pedestrian hears
- a) when the police car is approaching the
pedestrian?
- b) when the car is receding from the pedestrian?
Problem 7
-
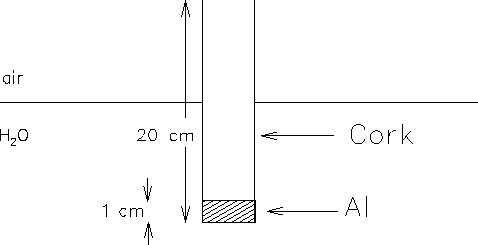 A cylindrical rod is formed from cork
(specific gravity = 0.25) and aluminum
(specific gravity = 2.7) cylindrical sections.
The lengths of the sections are 20.0 cm and
1.0 cm respectively. The rod is allowed to float
in Lake Matoaka, with the heavy end downwards.
A cylindrical rod is formed from cork
(specific gravity = 0.25) and aluminum
(specific gravity = 2.7) cylindrical sections.
The lengths of the sections are 20.0 cm and
1.0 cm respectively. The rod is allowed to float
in Lake Matoaka, with the heavy end downwards.
- a) In equilibrium, how much of the cylinder's length is
underwater?.
- b) [Extra credit question - do not attempt this part unless you have
finished the rest of the exam!] The cylinder is given a push, so that it
begins to bob up-and-down in the water. What is the frequency of the
resulting oscillation?
Problem 8
-
The polar ice caps of the earth contain 2 x 1019 kg of ice. Since
this ice is located at the poles, its contribution to the moment of inertia
of the earth is negligible. In a weird practical joke, the Klingon empire
arranges to have all of this ice moved to a single pile located on the
equator. The radius of the Earth = 6370 km, the mass of the Earth =
6.0 x 1024 kg, Isphere = (2/5)MR2.
- a) Would the length of the day become shorter or longer? Why?
- b) By how much?
Previous
Physics 101 Exams
Physics 101 Home page
Physics Department Home Page
College of William and Mary
armd@physics.wm.edu
last updated: Nov. 30 1999


 A flagpole of mass m and length L is hinged at
a wall and supported in a horizontal position by a
massless cable attached to the free end (see diagram).
The cable makes an angle
A flagpole of mass m and length L is hinged at
a wall and supported in a horizontal position by a
massless cable attached to the free end (see diagram).
The cable makes an angle  A cylindrical rod is formed from cork
(specific gravity = 0.25) and aluminum
(specific gravity = 2.7) cylindrical sections.
The lengths of the sections are 20.0 cm and
1.0 cm respectively. The rod is allowed to float
in Lake Matoaka, with the heavy end downwards.
A cylindrical rod is formed from cork
(specific gravity = 0.25) and aluminum
(specific gravity = 2.7) cylindrical sections.
The lengths of the sections are 20.0 cm and
1.0 cm respectively. The rod is allowed to float
in Lake Matoaka, with the heavy end downwards.