Problem 2:
A 60 kg block slides along the top of a 100 kg block with an acceleration a = 3 m/s2 when a horizontal force of 320 N is applied. The 100 kg block sits on a horizontal frictionless surface, but there is friction between the two blocks.
a) Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the blocks.
b) Find the acceleration of the 100 kg block (when it is still in contact with the other block).
Solution:
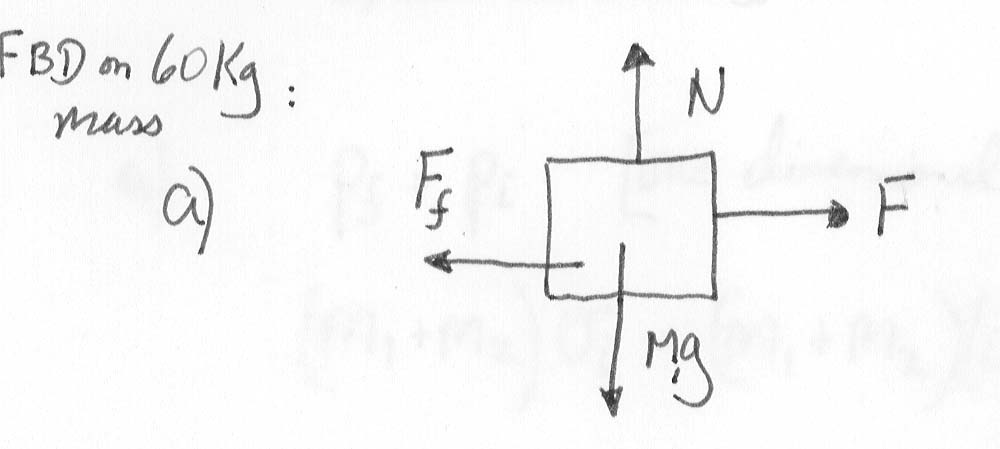
a) Draw a Free-body diagram for the 60 kg mass:

Now, apply F = m1a in both the x and y directions; we get
(x) F - Ff = m1 a
(y) N - m1g = 0 (no acceleration in y-direction)
and we have Ff = ![]() k
N =
k
N = ![]() k
m1g
k
m1g
so F - ![]() k
m1g = m1 a
k
m1g = m1 a
or ![]() k
= (F - m1a )/m1g =
[320 N - (60 kg)(3 m/s2)]/(60 kg)(9.8 m/s2)
= 0.238
k
= (F - m1a )/m1g =
[320 N - (60 kg)(3 m/s2)]/(60 kg)(9.8 m/s2)
= 0.238
b) The 100 kg is accelerated along by the frictional force.
Draw a Free-body diagram for the 100 kg mass:
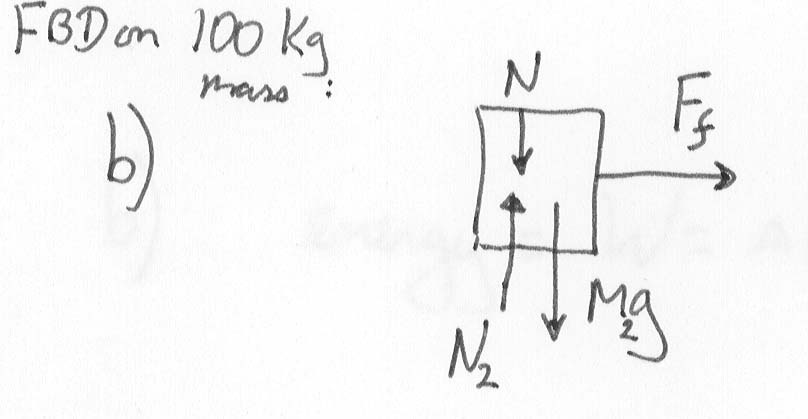
We can ignore the y-components, and concentrate on the x-component. The only force in this direction is the frictional force Ff, which is equal and opposite to the frictional force from part a) [Newton's 3rd Law!]. Thus
m2 a2 = Ff
= ![]() k
m1g
k
m1g
so
a2 = ![]() k
m1g / m2 = (0.238)(60 kg)(9.8
m/s2)/(100 kg)
k
m1g / m2 = (0.238)(60 kg)(9.8
m/s2)/(100 kg)
= 1.40 m/s2 (to the right)
Problem 3
Test 2
Physics 101 Home
page
Physics Department Home Page
College of William and Mary,
Dept. of Physics